What is Achilles Tendonitis? (Tendinitis)
Achilles heel pain is a common complaint our podiatrists encounter. It’s often referred to as achilles tendinopathy. It can be described as inflammation of the achilles tendon, or pathology of the achilles tendon.
The achilles tendon is the large tendon at the back of the lower leg that anchors the calf muscles to the heel bone (calcaneus). Repetitive use of the calf muscles and, subsequently, the achilles tendon can lead to microscopic tears within the substance of the tendon. To repair these microscopic tears, the body commences an inflammatory response.
The tendon will often present as swollen, painful and inflamed due to injury or most commonly, overuse. Pain can sometimes be replicated with tension or squeezing along the tendon at the back of the ankle or lower leg into the heel.
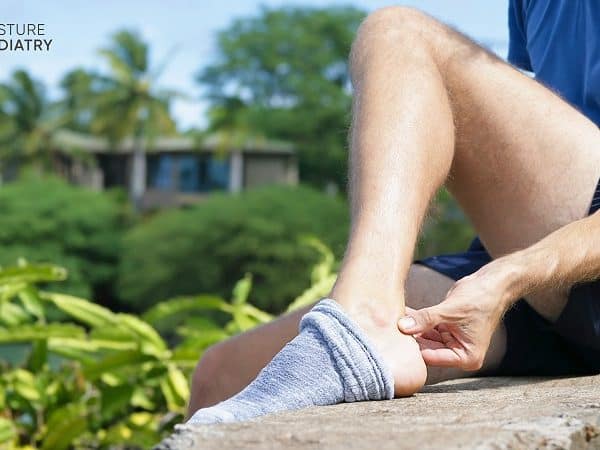

Early intervention and treatment is recommended as, left untreated, further injury can develop including tendon rupture or chronic achilles tendinosis. Achilles tendon injures can be painful and quite debilitating, often reducing free movement and restricting normal activities.
To schedule an appointment, call us on 8362 5900 or
BOOK ONLINE by clicking here
Is it Achilles Tendinitis, Achilles Tendinopathy or Achilles Tendinosis?…
What’s the Difference?
Achilles tendinitis, Achilles tendinopathy, and Achilles tendinosis are related conditions that involve inflammation and degeneration of the Achilles tendon, which is the large tendon connecting the calf muscles to the heel bone. While these terms are often used interchangeably, they have distinct characteristics:
- Achilles Tendinitis:
- Nature: “Tendinitis” implies inflammation of the tendon.
- Description: Achilles tendinitis refers to acute inflammation of the Achilles tendon. It is often characterised by pain, swelling, and stiffness around the tendon area.
- Causes: Typically caused by overuse, sudden increase in activity, or improper footwear. Activities that stress the tendon, such as running or jumping, can contribute to the development of tendinitis.
- Achilles Tendinopathy:
- Nature: “Tendinopathy” is a more general term that encompasses both inflammation and degeneration.
- Description: Achilles tendinopathy is a broader term that includes both inflammatory and degenerative changes in the tendon. It may involve chronic pain, swelling, and impaired function.
- Causes: Similar to tendinitis, tendinopathy can result from overuse, repetitive stress, or aging. It may also be associated with poor biomechanics or insufficient recovery time between activities.
- Achilles Tendinosis:
- Nature: “Tendinosis” specifically refers to degeneration without significant inflammation.
- Description: Achilles tendinosis is characterised by the degeneration of the collagen fibers within the tendon without the prominent inflammatory component seen in tendinitis. It is often associated with chronic, long-term conditions.
- Causes: Chronic tendinopathy that has progressed to a degenerative state. Factors such as repeated microtrauma, aging, and poor blood supply to the tendon can contribute to the development of tendinosis.

It’s important to note that these terms are sometimes used interchangeably in clinical practice, and the boundaries between them may not always be clear-cut. Additionally, proper diagnosis and treatment should be carried out by a healthcare professional, based on a thorough examination and possibly imaging studies like ultrasound or MRI.
Early intervention and treatment is recommended as, left untreated, further injury can develop including tendon rupture or chronic achilles tendinosis. Share on X
To schedule an appointment, call us on 8362 5900 or
BOOK ONLINE by clicking here
What Causes Achilles Tendonitis?
Common causes include:
- Overuse injury to the tendon. This occurs when the achilles tendon is loaded excessively and constantly stressed. Inflammation and swelling can occur as a result of the constant stress and small tears can also develop.
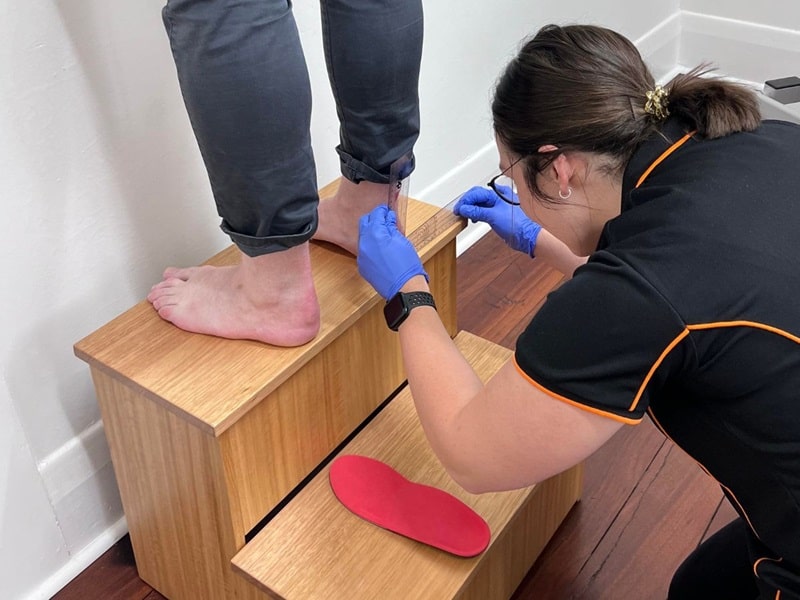
- Poorly functioning feet and an increase in mechanical stress through the achilles tendon. Flat feet (feet that turn inwards) create a bow of the tendon and creates a tight constant strain on the heel, resulting in painful inflammation. This abnormality should be neutralised using foot orthotics to reduce the strain on the tendon and to help stop recurrence of injury.
- Certain types of training and maximum load training may also lead to inflammation to the Achilles tendon. A sudden increase in training, excessive hill running, and speed work can also lead to inflammation of the achilles tendon. High load sports (i.e. basketball, netball) can also contribute to stress on the tendon. Jumping and high volume running can overload the achilles tendon and increase inflammation.
- Footwear choice is very important. Choosing the correct footwear which suits your foot type, your sport and your exercise level is vital. Wearing inappropriate shoes (minimal support) while walking or running can increase the risk of achilles tendonitis. Sandals and high heels can also increase the load through the tendon and potential for inflammation. Cushioned shoes or innersoles which are worn out can cause the heel to sink into the shoe and no longer provide sufficient shock absorption. This increased aggravation through straining and pulling the tendon can aggravate and trigger pain.
- Tight calf and hamstrings (posterior chain) may also contribute to prolonged achilles troubles. The continual strain they exert on the tendon could be inhibiting any treatment management options.
- Being overweight can also increase the risk of achilles tendonitis. Holistically, it can put a strain on all parts of the body. Often the increase in load and forces through the tendon can cause inflammation if stressed. This can be a vicious cycle as once the level of exercise increases, so does the load and strain which causes the pain which then ceases exercise levels.
- Inflammatory conditions like arthritis can cause achilles tendonitis. These can cause generalised inflammatory arthritis, such as ankylosing spondylitis or psoriatic arthritis.
To schedule an appointment, call us on 8362 5900 or
BOOK ONLINE by clicking here
Diagnosis of Achilles Tendonitis
If you have or suspect you have achilles tendinopathy, you should consult your podiatrist. Initially, it’s important to diagnose the problem and establish the severity. Once diagnosed, an appropriate treatment plan and time frame for improvement can be determined.
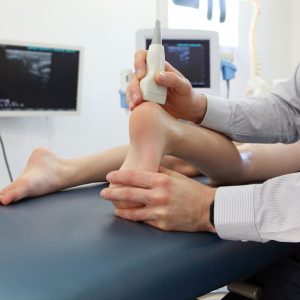
Assessment methods include:
- Medical and injury history – where, when, footwear, exercise habits, other important factors (job, previous/other injuries)
- Imaging may be requested – X-ray, ultrasound and potentially MRI scan of the problematic tendon(s). Occasionally blood tests can be used to assess inflammatory conditions
- Physical biomechanical examination and assessment – foot posture, gait analysis, hands on approach (thickness and tenderness of the tendon)
How is Achilles Tendonitis Treated?
Like many conditions, Achilles tendonitis responds well to early conservative treatment. If ignored and disregarded, the symptoms can continue, and the condition can become chronic. The aim is to reduce strain and load on the tendon and reduce inflammation, in turn, reducing pain.
Like many conditions, Achilles tendonitis responds well to early conservative treatment. Share on X
There is no solo treatment to reduce symptoms of achilles tendonitis, it is important to follow a specific treatment combination once the diagnosis has been confirmed.
To schedule an appointment, call us on 8362 5900 or
BOOK ONLINE by clicking here
Achilles tendonitis treatment and management strategies include:
- Training or Activity Modification. This is important to reduce strain on the achilles tendon. Whilst it is important to keep moving, the change of load (i.e. high volume jumping) will allow healing to commence. This will also aid in successful treatment and rehabilitation of the affected tendon. Avoiding activities that increase pain will reduce aggravation to the inflamed area.
- Heel raises are a temporary short-term measure. The aim is to decrease load and strain on the achilles tendon in the short term during tendon rehabilitation.
- Orthoses (shoe inserts) aid in the correction of body mechanics. The are designed to allow the foot to function within a desired range and to reduce excessive load or damaging forces. The aim is to realign the forces on the rear foot and to reduce tendon overload. This will help to promote healing in the longer term.

- Footwear choice can make a significant difference. Be sure to chat to your podiatrist about the right shoes for you. The wrong shoe choice can increase load on the achilles tendon.
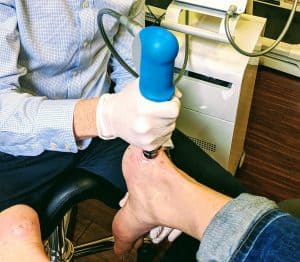
- Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) – This form of treatment is widely used for soft tissue conditions. ESWT is best used as part of the treatment plan for chronic conditions such as achilles tendinosis. ESWT helps to increase blood flow and healing to the chronically injured achilles tendon. Radial shock waves are high energy sound waves which help to increase blood flow and metabolic activity around the site of pain, accelerating the healing process. Shock wave therapy also effectively reduces pain by increasing analgesic effects in the area. Studies have shown best results are achieved by applying 3 to 4 treatments at 7 to 14 day intervals.
- Stretching and strengthening exercises will be prescribed where appropriate and will vary depending on whether your achilles tendon injury is acute or chronic. Correctly performed eccentric strengthening exercises may be appropriate for achilles tendinosis but not at all suitable for a ruptured achilles tendon. Progressive loading of the tendon is important in reducing inflammation, decreasing pain, and restoring strength and function. Ask your podiatrist about an appropriate eccentric loading program.
- Massage can help with restoring the extensibility of the tendon, increase strength and promote full recovery.
- Dry Needling/Trigger Point Therapy can also be very helpful as part of your treatment program.
- Anti-inflammatory medication is again, a short-term option. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can be used (if it is safe to do so) to reduce inflammation to the Achilles tendon.
- Surgery is only recommended if all other conservative treatment options have failed after a prolonged time. However, if the tendon has ruptured then surgery is necessary to re-attach the tendon.
To schedule an appointment, call us on 8362 5900 or
BOOK ONLINE by clicking here




