Understanding Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatment Options
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction (PTTD) may not be a household term, but it significantly impacts the lives of those who experience it. This condition occurs when the posterior tibial tendon, essential for foot support and stability, becomes inflamed or damaged.
Understanding the causes and symptoms of PTTD is key to addressing the discomfort and limitations it brings. From overuse and injury to underlying medical issues, a variety of factors can contribute to this dysfunction. Recognizing the early signs—such as pain along the inner foot or swelling—can be crucial for timely intervention. Fortunately, there are effective treatment options ranging from exercises, physical therapy, orthotics, footwear and bracing to surgical solutions, all designed to restore function and alleviate pain.
Whether you are dealing with PTTD or merely seeking information to support a friend or family member, this article will provide comprehensive insights, empowering you to take informed steps towards recovery and regaining mobility.
Need an Experienced Adelaide Podiatrist for PTTD or Ankle Pain?
Book Online 24/7 or Call 8362 5900
Anatomy of the Posterior Tibial Tendon
The posterior tibial tendon is a crucial component of the lower leg, running along the inside of the ankle and down into the foot. This tendon connects the calf muscles to the bones on the inside of the foot, playing a vital role in maintaining the arch and supporting the foot during movement. It is responsible for stabilizing the foot when walking or running and helps in the push-off phase of each step, making it essential for proper gait and mobility.
Understanding the anatomy of this tendon is important because any disruption in its function can significantly affect one’s ability to walk and perform daily activities. The posterior tibial tendon works in conjunction with other structures in the foot and ankle, including ligaments and bones, to provide balance and support. When the tendon is compromised, these interconnected systems are also affected, leading to a cascade of problems.
The tendon itself is composed of strong fibrous tissue that can withstand significant stress. However, like any other part of the body, it is susceptible to wear and tear over time. The posterior tibial tendon is particularly vulnerable due to its location and the amount of stress it endures during regular activities. Understanding its function and importance helps in recognizing why its dysfunction can lead to substantial mobility issues.
Need an Experienced Adelaide Podiatrist for PTTD or Ankle Pain?
Book Online 24/7 or Call 8362 5900
Common Causes of Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction (PTTD) can arise from various causes, often related to overuse, injury, or underlying health conditions. One of the most common causes is overuse or repetitive strain, especially in athletes and individuals who engage in high-impact activities. Continuous stress on the tendon can lead to microtears and eventual degeneration, compromising its ability to support the foot.
Injury is another significant cause of PTTD. A direct trauma to the tendon, such as a fall or a sudden twist of the ankle, can cause acute damage. This injury can result in inflammation, partial tears, or even a complete rupture of the tendon, leading to immediate pain and loss of function. Without proper treatment, these injuries can develop into chronic conditions, further complicating recovery.
Underlying medical conditions also contribute to the development of PTTD. Disorders such as diabetes, hypertension, and arthritis can affect the health of the tendon and surrounding structures. These conditions often lead to poor circulation, reduced healing capacity, and increased inflammation, making the tendon more vulnerable to injury and degeneration. Recognizing these contributing factors is essential for both prevention and treatment.
Need an Experienced Adelaide Podiatrist for PTTD or Ankle Pain?
Book Online 24/7 or Call 8362 5900
Recognizing the Symptoms of Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction
Early recognition of PTTD symptoms is crucial for effective treatment and preventing further damage. One of the primary symptoms is pain along the inside of the ankle and foot. This pain is often exacerbated by activity and may improve with rest, only to return with continued use. As the condition progresses, the pain may become more constant and severe.
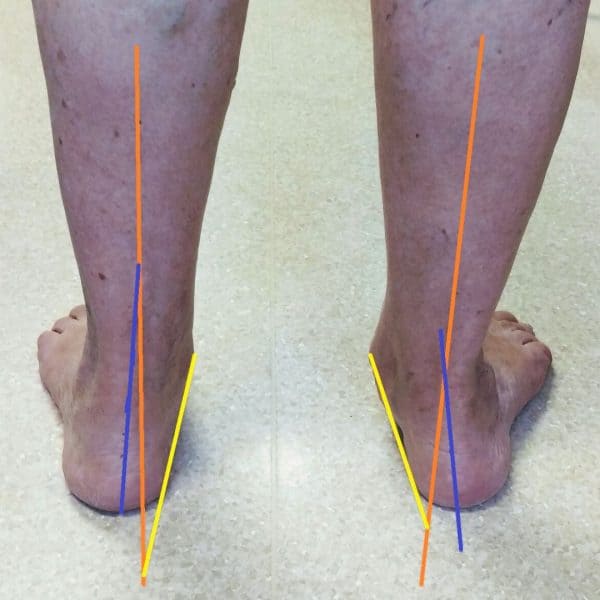
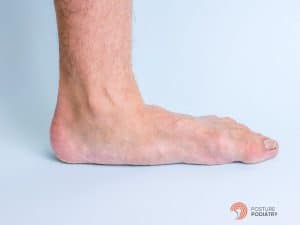
Swelling along the inside of the ankle is another common symptom. This swelling is often accompanied by tenderness and warmth, indicating inflammation. In more advanced cases, the arch of the foot may begin to collapse, leading to a flatfoot deformity. This change in the foot’s structure can further exacerbate pain and impair mobility, making it difficult to perform everyday activities.
Other symptoms include weakness in the foot and ankle, difficulty standing on tiptoes, and an increased tendency to roll the ankle inward. These signs indicate that the tendon is no longer functioning properly and that the stability of the foot is compromised. Recognizing these symptoms early can lead to timely intervention and better outcomes.
Need an Experienced Adelaide Podiatrist for PTTD or Ankle Pain?
Book Online 24/7 or Call 8362 5900
Risk Factors for Developing Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction
Several risk factors increase the likelihood of developing PTTD. Age is a significant factor, as the tendon naturally weakens and loses elasticity over time. Middle-aged and older adults are more prone to this condition, particularly if they have a history of foot or ankle problems. Gender also plays a role, with women being more susceptible to PTTD than men.
Obesity is another major risk factor. Excess body weight places additional stress on the posterior tibial tendon, increasing the likelihood of overuse injuries and degeneration. Individuals who are overweight or obese are at a higher risk of developing PTTD, particularly if they engage in high-impact activities or have poor footwear choices.
Certain medical conditions can also predispose individuals to PTTD. Diabetes, hypertension, and rheumatoid arthritis are known to affect tendon health and contribute to the development of this dysfunction. Additionally, individuals with flat feet or other structural abnormalities are at a higher risk, as these conditions place extra strain on the posterior tibial tendon.
Need an Experienced Adelaide Podiatrist for PTTD or Ankle Pain?
Book Online 24/7 or Call 8362 5900
Diagnosis: How is Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Identified?
Diagnosing PTTD involves a combination of clinical evaluation and imaging studies. The diagnostic process typically begins with a thorough medical history and physical examination. During the examination, the podiatrist will assess the foot and ankle for signs of swelling, tenderness, and deformity. They will also evaluate the range of motion and strength of the affected area.
Imaging studies are often necessary to confirm the diagnosis and determine the extent of the damage. X-rays can help identify changes in the foot’s structure, such as a collapsed arch or misalignment of the bones. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is particularly useful for visualizing soft tissue structures, including the posterior tibial tendon. An MRI can reveal inflammation, tears, and other abnormalities that may not be visible on an X-ray.
In some cases, an ultrasound may be used as an alternative to MRI. Ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging technique that can provide real-time images of the tendon and its movement. This method is particularly useful for assessing the dynamic function of the tendon and identifying areas of inflammation or degeneration. Together, these diagnostic tools help healthcare providers develop an accurate diagnosis and an effective treatment plan.
Need an Experienced Adelaide Podiatrist for PTTD or Ankle Pain?
Book Online 24/7 or Call 8362 5900
Treatment Options: Non-Surgical Approaches
Non-surgical treatment options are often the first line of defense for managing PTTD, especially in the early stages. One of the most common non-surgical treatments is physical therapy. Physical therapy focuses on strengthening the muscles and tendons that support the foot and ankle. Exercises are designed to improve flexibility, stability, and strength, helping to alleviate pain and prevent further damage.
Orthotic devices and bracing are also commonly used to manage PTTD. Custom orthotics can help support the arch and redistribute pressure away from the damaged tendon. Braces, such as ankle-foot orthoses (AFOs), can provide additional support and stability, reducing strain on the tendon and allowing it to heal. These devices are particularly useful for individuals with flat feet or other structural abnormalities.
Other non-surgical treatments include anti-inflammatory medications and corticosteroid injections. These treatments can help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain, making it easier to engage in physical therapy and other rehabilitative activities. In some cases, rest and activity modification may be necessary to allow the tendon to heal. This may involve avoiding high-impact activities and using supportive footwear to reduce strain on the tendon.
Need an Experienced Adelaide Podiatrist for PTTD or Ankle Pain?
Book Online 24/7 or Call 8362 5900
Surgical Treatment Options for Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction
When non-surgical treatments fail to provide relief or the condition is too advanced, surgical intervention may be necessary. There are several surgical options for treating PTTD, depending on the severity of the condition and the specific needs of the patient. One common procedure is tendon debridement, which involves removing damaged or inflamed tissue from the tendon to promote healing.
Tendon transfer is another surgical option for PTTD. This procedure involves transferring a healthy tendon from another part of the foot to replace the damaged posterior tibial tendon. This helps restore function and support to the affected area. In some cases, a calcaneal osteotomy may be performed in conjunction with a tendon transfer. This procedure involves cutting and realigning the heel bone to improve the foot’s structure and relieve strain on the tendon.
In more severe cases, a fusion procedure may be necessary. This involves permanently fusing the bones in the foot and ankle to provide stability and eliminate pain. While this procedure restricts movement in the affected area, it can be highly effective in relieving pain and preventing further damage. Each surgical option carries its own risks and benefits, and the choice of procedure will depend on the individual patient’s condition and treatment goals.
Need an Experienced Adelaide Podiatrist for PTTD or Ankle Pain?
Book Online 24/7 or Call 8362 5900
Rehabilitation and Recovery: What to Expect
Rehabilitation and recovery are critical components of the treatment process for PTTD. The goal of rehabilitation is to restore function, alleviate pain, and prevent future injuries. The recovery process typically begins with a period of rest and immobilization to allow the tendon to heal. This may involve wearing a cast or brace and avoiding weight-bearing activities.
Once the initial healing phase is complete, physical therapy becomes an essential part of the recovery process. Physical therapy focuses on gradually increasing the strength and flexibility of the foot and ankle. Exercises may include stretching, strengthening, and balance training. The therapist will also work on improving gait and functional activities to ensure a smooth return to daily activities.
The duration of the recovery process can vary depending on the severity of the condition and the type of treatment received. Non-surgical treatments may require several weeks to months of rehabilitation, while surgical treatments may require a longer recovery period. It is important for patients to follow their healthcare provider’s recommendations and adhere to their rehabilitation program to achieve the best possible outcomes.
Need an Experienced Adelaide Podiatrist for PTTD or Ankle Pain?
Book Online 24/7 or Call 8362 5900
Conclusion: Managing Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction for Long-Term Health
Managing PTTD for long-term health involves a combination of prevention, early intervention, and ongoing care. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and risk factors associated with this condition can help individuals take proactive steps to protect their foot and ankle health. Early recognition and treatment of symptoms are crucial for preventing further damage and ensuring a successful recovery.
For those at risk of developing PTTD, preventive measures such as maintaining a healthy weight, wearing supportive footwear, and avoiding high-impact activities can be beneficial. Regular exercise and stretching can help strengthen the muscles and tendons that support the foot and ankle, reducing the risk of injury. Individuals with underlying medical conditions should work closely with their healthcare providers to manage their health and reduce the risk of tendon dysfunction.
Ongoing care and monitoring are essential for individuals with PTTD to prevent recurrence and maintain long-term health. Regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider, adherence to a rehabilitation program, and lifestyle modifications can help manage symptoms and improve overall foot and ankle function. With the right approach, individuals with PTTD can achieve a pain-free and active lifestyle.
Need an Experienced Adelaide Podiatrist for PTTD or Ankle Pain?
Book Online 24/7 or Call 8362 5900